DISCO
Overall, the combined URBANopt™-DISCO workflow allows users to investigate the impacts of building loads and colocated distributed energy resource (DER) strategies on electric distribution system performance and required network upgrades. For example, the URBANopt-DISCO capabilities can help understand the value of building energy efficiency and demand flexibility in upgrade and new/load growth scenarios at a neighborhood/district/community scale based on power flow solutions.
DISCO Background
DISCO (Distribution Integration Solution Cost Options) is an open-source, NLR-developed, python-based software tool for automating distribution analyses at scale. Originally developed to support photovoltaic (PV) impact analyses, DISCO can also be used to understand the impact of other DERs on distribution substations/feeders. DISCO, as a framework is based on power flow modeling with OpenDSS as the grid simulation engine. PyDSS, another NLR developed tool, is used to interface with OpenDSS and provide additional control layers on DERs.
DISCO combines many features in forms of analysis modules such as snapshot and dynamic hosting capacity analysis, grid impact analysis, automated upgrade cost analysis, and cost-benefit analysis for selected grid control strategies.
URBANopt-DISCO Workflow
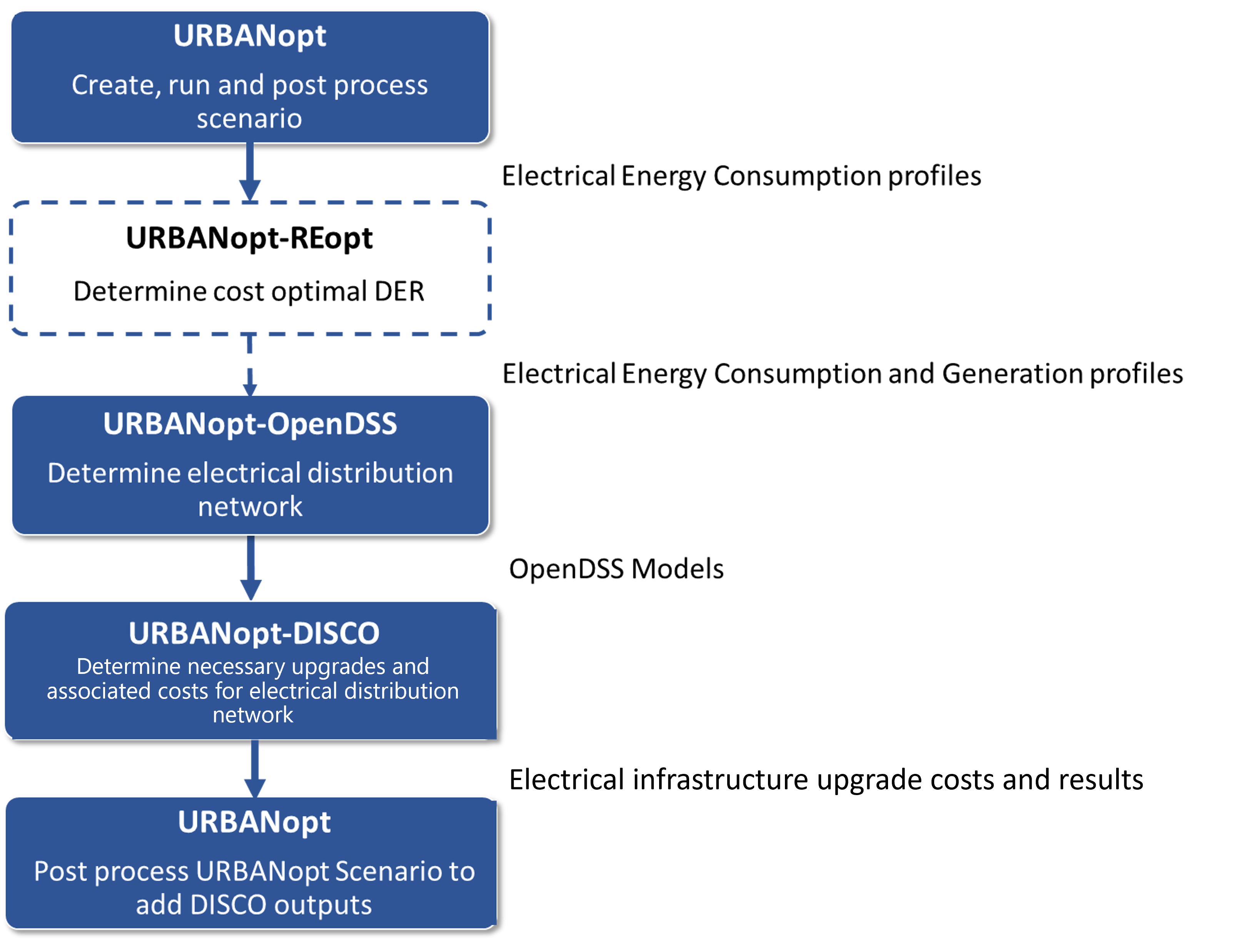
The URBANoptTM-DISCO workflow leverages the automated upgrade cost analysis module within the DISCO pipeline to determine the distribution system upgrades required to mitigate any voltage and thermal violations that exist on a distribution feeder and then calculate the cost associated with those upgrades. These network upgrades currently include traditional infrastructure upgrade options (reconductoring, upgrade transformers, installing voltage regulators and capacitor banks, and changing the controls or setpoints on voltage regulators and capacitor banks).
Prior to running the DISCO analysis, the URBANopt-OpenDSS workflow is used to create OpenDSS models for the distribution system. These OpenDSS models represent the distribution grid’s operational baseline in terms of power flow solutions. Network models in OpenDSS, along with the cost database file and technical catalog for distribution system equipment are passed on to DISCO (more details about these inputs are provided below). Several URBANopt scenarios can be defined to represent the district with varying amounts of building efficiency, building demand flexibility, PV penetration, and battery storage. These scenarios are designed to provide variations in building loads which are used in power flow simulations within DISCO to analyze overall grid impacts.
The DISCO module loops through these scenarios and analyzes the thermal and voltage violations to determine the grid infrastructure upgrades required, if any, and reports the associated costs in each case.
An overview of the URBANopt-DISCO workflow is shown below:
DISCO Installation
Visit the DISCO Installation page to install DISCO.
Usage
The DISCO workflow is available via the disco URBANopt CLI command.
For in-terminal help:
uo disco --help
In order to use the URBANopt-DISCO capabilities, the DISCO Project can be created and run using the URBANopt CLI following the steps below:
-
Create a DISCO Project
Create a DISCO project by including the
-aflag in the create command:uo create --project-folder <path/to/disco/folder> --discoThis will create a
discofolder in the URBANopt example project which includes DISCO specific files such as thecost_database.xlsx,technical_catalog.jsonand theconfig.jsonfile. A description of these files is provided below.-
cost_database.xlsx: This is a customizable cost database containing technical specifications and associated per unit upgrade costs for electrical network equipment such as lines, transformers etc. Users can customize and/or create their own databases of proprietary equipment costs if they wish to do so to reflect the costs and available equipment of the distribution system they are looking to represent. The cost database used in DISCO is based on the catalog of equipment used to create synthetic network designs in the URBANopt-RNM workflow. -
technical_catalog.json: The technical catalog contains the detailed electrical specifications of the equipment that is represented in thecost_database.xlsxfile. The components used are those specified in the URBANopt-RNM Module equipment catalog. -
config.json: This configuration file specifies the DISCO analysis jobs to be run for the analysis, and also defines the input technical parameters for the simulation.
The DISCO example project also includes the
example_project_with_electric_network.jsonFeature File that contains the building features as well as the electrical distribution network of a given district. -
-
Create Scenario Files
Scenario files are created next. If using the URBANopt-REopt workflow, scenario files for REopt need to be created. More details on creating scenario files are provided under the Set up Scenario section.
uo create --scenario-file <path/to/FEATUREFILE.json> -
Run the Project
Run the project using the DISCO feature file, and the scenario file created in the previous step:
uo run --feature <path/to/DISCO/featurefile.json> --scenario <path/to/SCENARIOFILE.csv> -
Default post-process Scenario
Post-process using the default post-processor:
uo process --default --feature <path/to/FEATUREFILE.json> --scenario <path/to/SCENARIOFILE.csv>Or, post process using the REopt Feature Post-Processor if using the REopt workflow.
uo process --reopt-scenario --feature <path/to/FEATUREFILE.json> --scenario <path/to/SCENARIOFILE.csv> -
Run OpenDSS
To run OpenDSS, use the OpenDSS command and specify detailed options or a config JSON file with pre-specified options. For more details on running OpenDSS refer to the OpenDSS documentation.
To access the list of all the options:
uo opendss -hExample
opendssCLI call:uo opendss --feature <path/to/FEATUREFILE.json> --scenario <path/to/SCENARIOFILE.csv>An example
opendssCLI call using a config JSON file: ```bash uo opendss –config path/to/config.json -
Run DISCO
To run use the DISCO command and specify the DISCO Feature File and Scenario file.
Additional options namely the custom cost database and the technical catalog can also be specified. Details on all DISCO options can be viewed using the
-hflag as shown below:uo disco -hThis prints out the following options and their descriptions:
--scenario— Required, Path to scenario csv file
--feature— Required, Path to feature json file
--cost_database— Optional, Filename for custom cost database
--technical_catalog— Optional, Filename for custom technical catalog -
Post-Process DISCO results
To integrate DISCO results into URBANopt Scenario Reports, use the DISCO post-process as shown:
uo process --disco --feature <path/to/FEATUREFILE.json> --scenario <path/to/SCENARIOFILE.csv>The DISCO results are summarized under
scenario_power_distribution_costkey in the scenario_report_disco.json file in the scenario results folder. The DISCO results reported are:results:
-num_violations: Number of violations present in the feeder after upgrades cost analysis is completed.
-total_cost_usd: Total cost (in US dollars) needed to upgrade the feeder to mitigate violations.outputs: This points the user to the
run_upgrade_cost_analysis.logfile path and includes detailed output files for each job.violation_summary: This provides a summary of number and magnitude of all violations, both before and after thermal and voltage upgrades. Users can refer to it if they want to get a better understanding of the impacts on feeder power quality at various stages of the automated upgrades cost analysis.
costs_per_equipment: This gives costs for each upgraded piece of equipment.
equipment: This is a list of all equipment in the feeder with information on whether it has been upgraded as well as details on any changed parameters.
A DISCO folder containing detailed results is also created within the outputs folder for the scenario and contains the following:
job_outputs: This folder contains sub-folders for each job. Each job folder has the upgraded OpenDSS files as well detailed feeder statistics in case the user wants to delve deeper into the technical aspects of the feeder.run_upgrade_cost_analysis.log: Contains detailed run log for the DISCO simulation includingINFOandERRORmessages. More details on debugging the error codes.
upgrade_summary.json: This file reports out the DISCO results for the analysis. It contains information on results, violation_summary, costs_per_equipment and equipment which have been described above.More documentation on the DISCO automated upgrades cost analysis.